大人気のMastodon。この流れにのって自分でもインスタンスを立ち上げてみました。
ただ力不足で、確認メールを送信するところがまだ出来ていない。本当にすまない。
そのあたりも後述しますが、まだ理解できてないところも多いです。しかし、ここまででも他の人の参考になればと思い公開します。
目次
Mastodonとは
この一週間くらいで一気に流行始めたSNSサービスです。Mastodon自体はサービスを提供するプログラムであり、それを使って個人や企業がインスタンス(Mastodonのサービスを提供しているサーバのこと)を立てていっているのが現状。個人だとmstdn.jp、企業はpawoo.netやfriends.nicoが有名かしら。
インスタンスに登録するところは別サイトになりますが、以前記事に書きました。よろしければこちらもどうぞ。
Mastdonインスタンスを作るには
インスタンスを作る方法として、現在大きく二種類あります。
・Mastodonのプログラムをインストールして作る
・Dockerコンテナを利用する
Dockerはいわば動作環境ごとセットになっているパッケージのようなものですね。ただ、そのDockerを動かすための環境構築が必要でもあります。
ここでは、環境を整えてMastodonプログラムをインストールするところからやってみます。
なぜインスタンスを自分で立てるのか
私個人としては、ただの技術的興味が一番の理由になります。
でもMastodonを使っていく場合に、お一人様インスタンスを立てて自分のメインアカウントを管理することになっていくかもしれないと思うところもあり、立て方くらいは調べておこうかなと思ったところもあります。
それぞれのインスタンスにアカウントを取るのが良いのか、リモートフォローを活用していくのが良いのか、まだちょっと分からないですが。
そもそも仮想サーバーの維持費が安いプランでも月500円かかるので、続けていくかもわからない。mstdn.jpとかに大人しく定住するのがいいのかもしれない。
インスタンスを立てるための環境
環境として用意したのは次の通り。
グローバルIPアドレスのあるCentOS7サーバー
外部からアクセスのできるサーバー環境が必要です。
こちらもとりあえず、IDCFクラウドにアカウントを持っていたので、そちらに仮想環境を作りました。
サーバーはlight.S1で月500円。試すには十分ですが、途中で少しメモリが足りなくなってしまいましたので、スワップを追加する設定を行いました。
外部からアクセスできるように、ssh、http, https、3000をポートフォワードしておきます。
sshは作業用に、ポート3000はMastodonのテスト用に使います。
httpは、httpでアクセスが来たときにそれを受けて、httpsにリダイレクトするために開けておきます。
Mastodon用ドメイン
Mastodonを動かすためのドメインです。
私はお名前.com ![]() に自前ドメイン(scriptlife.jp)を持っていたので、そこにmastodon.scriplife.jpを追加しました。
に自前ドメイン(scriptlife.jp)を持っていたので、そこにmastodon.scriplife.jpを追加しました。
試すだけならグローバルIPアドレスだけでも動かせそうでしたので、必須ではないです。
MastodonをCentOS7にインストールする
CentOSに環境を作り、動作させていきます。
ここから先の作業については次のURLを参考にしました。参考にしましたというか先に白状しておきますと手順とか設定とか正直なところQiita記事の受け売りみたいなものになっているかもしれないところがあり本当にすまない。Rubyとかrailsとか、その他にも触ったことないサービスが多くて結局言われるままなんよ…
Qiitaの記事では最新版をいろいろなところから集めてきますが、私は標準に入っているものはそのまま使うスタンスでやってみています。
OSのインストールとアップデート
まずOSのインストール。仮想サーバーであれば、インストール済みの状態で用意されます。OSはCentOS7を選択します。
そして、入っているパッケージをひとまずアップデートします。
# yum update # reboot
必要なパッケージのインストール
必要なパッケージをがしがしインストールしていきますよ。
ImageMagick
# yum install ImageMagick
FFMpeg
# yum install https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/el/rpmfusion-free-release-7.noarch.rpm # yum install ffmpeg
FFMpegはrpmfusionからインストールします。こいつをソースコードからインストールしようとしたらめっさ苦労するから大人しくrpmを使うがよい…
Redis
# yum install epel-release # yum install redis
こちらもepelを追加してインストール。
インストール後に、サービスとして起動するようにします。
# systemctl start redis # systemctl enable redis
参考にした記事では「systemctl start redis && systemctl enable $_」となっていたところを分かりやすいようにバラしてみました。「$_」は「前のコマンドの最後の引数」となります。
PostgreSQL
# yum install postgresql-{contrib,devel,server}
# postgresql-setup initdb
# systemctl start postgresql
# systemctl enable postgresql
デフォルトのバージョン (9.2)でインストール。
Mastodon用ユーザーを作成します、
# sudo su - postgres -c 'psql -c "CREATE USER mastodon CREATEDB;"'
ここでsudoをいれてやらないと、
PostgreSQLを"root"で実行することはできません。システムセキュリティの危険防止のため非特権ユーザIDでサーバを起動しなければなりません。適切なサーバの起動方法に関する詳細はドキュメントを参照してください
と警告されますからpostgresになって実行します。
次に統計情報を有効にします。始めは要らないかなと思ったのですが、管理画面のPgHeroで「Query stats must be enabled for slow queries」と警告されたので有効にしました。
/var/lib/pgsql/data/postgres.confを修正します。
#shared_preload_libraries = '' # (change requires restart)
となっているところを、
shared_preload_libraries = 'pg_stat_statements' # (change requires resta rt) pg_stat_statements.track = all
とします。
変更したらリロードします。
# systemctl restart postgresql
Nginx
# yum install nginx
epelにあるようなのでそれを使います。
Ngnxは、MastodonをSSL化するためのプロキシ的な使い方をするみたい。
※ここではインストールするだけで、起動はさせません。後述するLet's Encryptの設定で独自にHTTPSを使用するので、起動しているとむしろ邪魔になるかもしれません。
Node.js
# curl -sL https://rpm.nodesource.com/setup_6.x | bash # yum install nodejs
標準バージョンは6.10.1のようで、それを使います。
setup_6.xを実行するのはお約束? Node.jsがまだよく分かっていないところある。
Yam
# curl -sL https://dl.yarnpkg.com/rpm/yarn.repo -o /etc/yum.repos.d/yarn.repo # yum install yarn
Yarnは専用リポジトリから。
Ruby
標準では2.0ですが、2.4.1が必要みたいなので、そちらを入れます。
ここではrvenvを使用して、mastodonユーザーに2.4.1環境を作ります。
Mastodonインスタンスはこのmastodonユーザーで動作させることになります。
(以降、rootユーザーとmastodonユーザーで操作する場面が混在していきます。コンソールが#の場合はroot、mastodon$ となっていたらmastodonユーザーと考えて下さい)
# yum install bzip2 gcc-c++ git {openssl,readline,zlib}-devel
# useradd mastodon
# su - mastodon
mastodon$ git clone https://github.com/rbenv/rbenv.git ~/.rbenv
mastodon$ cd ~/.rbenv && src/configure && make -C src && cd ~
mastodon$ echo 'export PATH="$HOME/.rbenv/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bash_profile
mastodon$ echo 'eval "$(rbenv init -)"' >> ~/.bash_profile && source ~/.bash_profile
mastodon$ git clone https://github.com/rbenv/ruby-build.git ~/.rbenv/plugins/ruby-build
mastodon$ rbenv install 2.4.1 && rbenv global $_ && rbenv rehash
これで、mastodonユーザーであれば2.4.1が使えるようになりました。
Bundler
mastodon$ gem install bundler
そのままmastodonユーザーで実行します。
Mastodonのインストール
いよいよインストール。
パッケージのダウンロード
パッケージをgithubから取得してきます。
mastodon$ cd ~ && git clone https://github.com/tootsuite/mastodon.git live && cd live mastodon$ git checkout $(git tag | tail -n 1) mastodon$ bundle install --deployment --without development test mastodon$ yarn install
/home/mastodon/liveにインストールされました。
設定の変更
mastodon$ cp .env.production.sample .env.production
liveの下に設定ファイルを作ります。.env.production.sampleを.evn.productionにコピーして、.env.productionの項目を修正します。
# Service dependencies REDIS_HOST=redis REDIS_PORT=6379 # REDIS_DB=0 DB_HOST=db DB_USER=postgres DB_NAME=postgres DB_PASS= DB_PORT=5432 # Federation LOCAL_DOMAIN=example.com LOCAL_HTTPS=true
となっているところを、
# Service dependencies REDIS_HOST=localhost REDIS_PORT=6379 # REDIS_DB=0 DB_HOST= DB_USER=mastodon DB_NAME=mastodon DB_PASS= DB_PORT=5432 # Federation LOCAL_DOMAIN=mastodon.scriptlife.jp:3000 LOCAL_HTTPS=false
とします。
DB_HOSTを空にすると、ローカルのpostgresを参照しにいきます。
LOCAL_DOMAINはmastodonを動かしているサーバーを指定します。まずテスト用に、ポート3000で起動させるので「mastodon.scriptlife.jp:3000」としています。LOCAL_HTTPSはテスト用にfalseにしておきます。
その下にある、
PAPERCLIP_SECRET= SECRET_KEY_BASE= OTP_SECRET=
については、
mastodon$ rake secret
を実行して、生成された文字列を指定します。ひとつの項目につき1回、都合3回生成します。
セットアップ
mastodon$ bundle exec rails db:setup RAILS_ENV=production mastodon$ bundle exec rails assets:precompile RAILS_ENV=production
railsでデータベースの設定と、アセットのプリコンパイルを行います。
サービス化
3つのサービスを実行するようにします。これはrootで行います。
それぞれサービス用の設定を作成し、systemctlで管理できるようにします。
mastodon-web (Puma)
Webサービスを作成、実行します。
/etc/systemd/system/mastodon-web.serviceに次のファイルを作成します。
[Unit] Description=mastodon-web After=network.target [Service] Type=simple User=mastodon WorkingDirectory=/home/mastodon/live Environment="RAILS_ENV=production" Environment="PORT=3000" ExecStart=/home/mastodon/.rbenv/shims/bundle exec puma -C config/puma.rb TimeoutSec=15 Restart=always [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
mastodon-sidekiq (Sidekiq)
/etc/systemd/system/mastodon-sidekiq.serviceに次のファイルを作成します。
[Unit] Description=mastodon-sidekiq After=network.target [Service] Type=simple User=mastodon WorkingDirectory=/home/mastodon/live Environment="RAILS_ENV=production" Environment="DB_POOL=5" ExecStart=/home/mastodon/.rbenv/shims/bundle exec sidekiq -c 5 -q default -q mailers -q pull -q push TimeoutSec=15 Restart=always [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
mastodon-streaming
/etc/systemd/system/mastodon-streaming.serviceに次のファイルを作成します。
[Unit] Description=mastodon-streaming After=network.target [Service] Type=simple User=mastodon WorkingDirectory=/home/mastodon/live Environment="NODE_ENV=production" Environment="PORT=4000" ExecStart=/usr/bin/npm run start TimeoutSec=15 Restart=always [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
サービスの自動起動
各サービス用の設定を作成したら、サービスの起動と自動起動の設定をします。
# systemctl start mastodon-web # systemctl start mastodon-sidekiq # systemctl start mastodon-streaming # systemctl enable mastodon-web # systemctl enable mastodon-sidekiq # systemctl enable mastodon-streaming
まとめてやるとなぜか上手くいかなかったので、ひとつずつコマンドを実行しました。
Query Statusの有効化
# sudo su - postgres -c 'psql -d mastodon -c "CREATE extension pg_stat_statements;"' # sudo su - postgres -c 'psql -d mastodon -c "SELECT pg_stat_statements_reset();"'
SELinuxの無効化
厄介の種なので基本オフにするバッドノウハウ。
# setenforce 0
とします。
IDCFのテンプレートではデフォルトでDisableだったので、特にすることはありませんでした。
kagucho.netで使用されているSELinuxのポリシーが公開されているようなので、有効にする場合はこちらを参考にするとよいかもしれません。
firewalled
IDCFの仮想マシンは、そもそもFWの内側にいて接続を制限されていますが、流れに沿って一応設定をしておきます。
firewalledはCentOS7より、iptablesに変わって標準になったFirewallサービスのよう。
こちらもデフォルトではオフになっていたようで、「FirewallD is not running」と言われてしまったのでサービスを起動するところから。
# systemctrl start firewalld # systemctrl enable firewalld
で、httpとhttpsを開けます。SSHはデフォルトで開いていたので、そちらはそのままで。
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service={http,https} && firewall-cmd --reload
※MastodonはHTTPSで通信を行いますが、ファイアウォールの設定ではHTTPも開けておきます。http://mastodon.scriptlife.jpでアクセスがきたときに、httpsにリダイレクトさせるためです。
リダイレクト設定は、後述するNginxで行います。
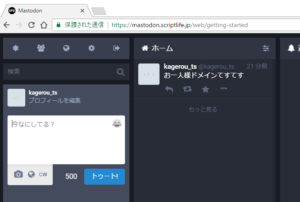
Mastodonの動作確認をする
ここまで来たら、仮ではありますが動作しているはず。
ポート3000を一時的に開けて、
# firewall-cmd --add-port=3000/tcp
http://mastodon.scriptlife.jp:3000 にアクセスしてみます。
やったぜ。
管理者の設定をする
管理者アカウントの設定をします。
管理者アカウントを作成するとき、Mastodonでは一般アカウントから昇格させることになるので、まずは一般アカウントを登録する必要があります。
つまり、まずは一般アカウントが存在する必要がありますが、この時点では登録確認メールが送信できていないので、普通に登録ができません。ですから「ユーザー名などを入力して登録 → そのメールアドレスをコマンドから承認 → そのユーザーを管理者に昇格」という手順を踏むことになります。
まずはMastodonのサイト画面から普通に登録を行います。登録するユーザー名は「admin」、メールアドレスは「admin@gmail.com」と仮にします。
で、次にmastodonアカウントのliveディレクトリ以下で、
mastodon$ RAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rails mastodon:make_admin USERNAME=admin mastodon$ RAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rails mastodon:confirm_email USER_EMAIL=admin@gmail.com
として、そのアカウントを管理者に昇格させ、メールの確認も行ったことにします。
これでadmin@gmail.comでログインできるようになっているはず。
またログインしてみると、「設定」のところに「管理」項目が増えており、そこから管理用の設定ができるようになっています。
ひとまずは「サイト設定」にある、「新規登録を受け付ける」をオフにしておくとよいかもしれません。「有効」をクリックしたら「無効」に変わります。
確認用の設定をオフにする
Mastodon自体はそのままポート3000で動いていますが、外部から接続できないようにします。
# firewall-cmd --reload
とすると、ポート3000が閉じられます。(元に戻る)
.evn.productionの設定も修正する
.env.productionにしていた、テスト用の設定も戻しておきます。
LOCAL_DOMAINとLOCAL_HTTPSを、それぞれ次のようにします。
LOCAL_DOMAIN=mastodon.scriptlife.jp LOCAL_HTTPS=true
変更をしたらサービスを再起動します。
# systemctl restart mastodon-web
どうやらmastodonは、コードや設定を変更したら、サービスを再起動しないと反映されないようです。
rubyのwebサービスだからブラウザをリロードすればよいかと思っていたけど、サービスとして動作しているから、再起動してやらないといけないみたい。
関連している機能によって再起動するサービスが変わってくるので注意が必要です。
よくわからなかったら、
# systemctl restart mastodon-web # systemctl restart mastodon-sidekiq # systemctl restart mastodon-streaming
と全部のサービスを再起動してしまうのもアリ。
HTTPS化の設定
実際に動かす際にはHTTPSで通信させるようにします。
SSLの証明書についてはLet's Encryptを使用します。
作業自体は簡単なのですが、これを行うには独自のホスト名が必要になります。
# yum install certbot # certbot certonly --standalone -d mastodon.scriptlife.jp
「mastodon.scriptlife.jp」のところに、Mastodonサーバーのホスト名を指定します。
するとこのホスト名向けのSSL証明書を自動的に作ってくれます。
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to cancel):webmaster@scriptlife.jp Starting new HTTPS connection (1): acme-v01.api.letsencrypt.org ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Please read the Terms of Service at You must agree in order to register with the ACME server at ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- (A)gree/(C)ancel: a ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, a founding partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit organization that develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about EFF and our work to encrypt the web, protect its users and defend digital rights. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- (Y)es/(N)o: n
「webmaster@scriptlife.jp」のところには管理者のアドレスを入れます。(私はプライベートなgmailアドレスを入れておきましたが、それで通りました)
最後の「Would you be willing to ~」ではYにするとEFFのメーリングリストに登録してくれるようです。
作業中にcertbotがHTTPS通信を行うので、ApacheやNginxなどが起動してHTTPS(443)を使用していないか、ポート443がFWなどで接続できなくなっていないかは注意して下さい。
443で接続できないと、以下のようになります。
Failed authorization procedure. mastodon.scriptlife.jp (tls-sni-01): urn:acme:error:connection :: The server could not connect to the client to verify the domain :: Failed to connect to 210.152.246.61:443 for tls-sni-01 challenge IMPORTANT NOTES: - The following errors were reported by the server: Domain: mastodon.scriptlife.jp Type: connection Detail: Failed to connect to 210.152.246.61:443 for tls-sni-01 challenge To fix these errors, please make sure that your domain name was entered correctly and the DNS A record(s) for that domain contain(s) the right IP address. Additionally, please check that your computer has a publicly routable IP address and that no firewalls are preventing the server from communicating with the client. If you're using the webroot plugin, you should also verify that you are serving files from the webroot path you provided. - Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so making regular backups of this folder is ideal.
成功するとこう。
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Starting new HTTPS connection (1): acme-v01.api.letsencrypt.org Obtaining a new certificate Performing the following challenges: tls-sni-01 challenge for mastodon.scriptlife.jp Waiting for verification... Cleaning up challenges Generating key (2048 bits): /etc/letsencrypt/keys/0000_key-certbot.pem Creating CSR: /etc/letsencrypt/csr/0000_csr-certbot.pem IMPORTANT NOTES: - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at /etc/letsencrypt/live/mastodon.scriptlife.jp/fullchain.pem. Your cert will expire on 2017-07-21. To obtain a new or tweaked version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot again. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run "certbot renew" - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
失敗した場合は、もう一度「 certbot certonly --standalone -d mastodon.scriptlife.jp」を実行しなおせば良いです。
Nginxの設定と起動
仕組みとしてはどうも、ローカルのポート3000で動作しているMastodonサーバーのプロキシとしてNginxが動作して、HTTPS化をしているようです。
/etc/nginx/conf.d/mastodon.conf を以下のように作成します。
map $http_upgrade $connection_upgrade {
default upgrade;
'' close;}
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name mastodon.scriptlife.jp;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
listen [::]:443 ssl;
server_name mastodon.scriptlife.jp;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers EECDH+AESGCM:EECDH+AES;
ssl_ecdh_curve prime256v1;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/mastodon.scriptlife.jp/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/mastodon.scriptlife.jp/privkey.pem;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/mastodon.scriptlife.jp/chain.pem;
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
keepalive_timeout 70;
sendfile on;
client_max_body_size 0;
root /home/mastodon/live/public;
gzip on;
gzip_disable "msie6";
gzip_vary on;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_buffers 16 8k;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload";# add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'none'; style-src 'self'; script-src 'self' https://example.com; img-src 'self' https://example.com; connect-src 'self' wss://example.com; font-src 'self'; frame-ancestors 'none'; media-src 'self';";
location / {
try_files $uri @proxy;
}
location @proxy {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto https;
proxy_set_header Proxy "";
proxy_pass_header Server;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:3000;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
tcp_nodelay on;
}
location /api/v1/streaming {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto https;
proxy_set_header Proxy "";
proxy_pass http://localhost:4000;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
tcp_nodelay on;
}
error_page 500 501 502 503 504 /500.html;}
mastodon.scriptlife.jpを、それぞれ読み替えてもらえれば良いです。
ssl_certificate、 ssl_certificate_key 、 ssl_trusted_certificate でLet's Encryptのファイルを参照するようになっています。「/etc/letsencrypt/live/(ホスト名)」に作られているので、そちらを参照するようにして下さい。
できたら起動。
# systemctl start nginx # systemctl enable nginx
これで、https://mastodon.scriptlife.jpで接続できるようになりました!
定時処理の登録
mastodonユーザーのcrontabに、定時処理を書きます。
mastodon$ crontab -e
として開いたところに、
RAILS_ENV=production @daily cd /home/mastodon/live && /home/mastodon/.rbenv/shims/bundle exec rake mastodon:daily > /dev/null
を追記。
@dailyで日次処理してくれるのか…(今頃知るおっさん
確認メールの送信
で、ここが今詰まっているところです。
Mastodonは標準では、mailgunを利用してメールを送ることができるようになっているみたい。このサービスは1万通までは無料みたいなので、登録してみてもよかったのですが、そもそもCentOS7だとローカルにpostfixがあるのでそっちで送れないかなあと試しているところ。ですがまだ上手くいっていない。
Gmailが使えるらしいとの情報もあるので、そちらも試してみたい。
(2017/04/26追記 ひとまず出来たので記事にしました)
Mastodon(マストドン)の確認メールを自前メールサーバー(postfix)で送信する
railsやサービスとしての動作への理解も足りていないので、そのあたりを勉強しつつ、また追記していければと思っています。
でもとりあえずここまででも、何かの参考になれば。





コメント
2個目のインスタンスを導入中です。
参考にさせていただきました。
メールは同サーバー内にPostfixを立ち上げて使っています。
キモは、Mastodon側の「.env.production」ファイルの
SMTP_SERVER=
の部分でここのIPはlocalhostではなく、ifconfigで使っている内部IPを確認して設定することでMastodonから接続できるようになりました。
以上、今後ともよろしくお願いいたします。
@rinmon@mstdn.top
なるほど、情報ありがとうございます!
試してみます!
どうやらウチの引っかかりポイントはこことは違ったみたいでしたが、
いろいろと見直してみて解決することができました。
ありがとうございました!
[…] Mastodon(マストドン)のインスタンスをCentOS7で立ててみる 同じくさくらのスタートアップスクリプトを利用せずにインスタンスを立てる方法が書かれています。 […]
こちらの手順に従って構築しました。
特に悩むこともなく立ち上がりました。
大変感謝しております、ありがとうございます。
コメントありがとうございます。お役に立ててよかったです。
[…] http://scriptlife.hacca.jp/contents/programming/2017/04/23/post-2268/#i-9 mastodonの調査(特徴・起動・APIアクセスなど)メモ・・docker […]
[…] Mastodon(マストドン)のインスタンスをCentOS7で立ててみる […]